Exchange databases run a defragmentation process once a day by default. This process rearranges mailbox store and public folder store data more efficiently, eliminating unused storage space. Exchange database online defragmentation occurs automatically as part of the database maintenance process. Online defragmenting is performed automatically at 2:00 AM every day by default. Online defragmentation makes additional database space available by detecting and removing database objects that are no longer being used. The defragmentation process provides more database space without actually changing the file size of the database.
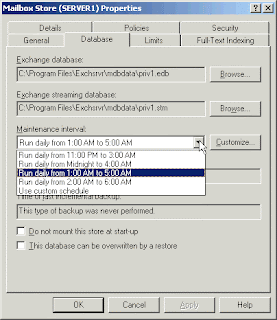
The following are two ways to schedule database defragmentation:
1. To schedule database defragmentation for an individual database, on the Database tab of a mailbox store or public folder store object, configure the maintenance interval using the Maintenance interval option.
2. To schedule database defragmentation for a collection of mailbox stores and public folder stores, on the Database (Policy) tab of a mailbox store or a public folder store policy, configure the maintenance interval using the Maintenance interval option.
Although online defragmentation provides some additional database space, you should also defragment your Exchange database offline to reduce the physical size of your Exchange database. You can perform offline defragmentation by using the ESE utility (ESEUTIL) while your mailbox stores and public folder stores are offline.
You would perform offline defragmentation, for instance, if you had recently moved a large number of users from a server running Exchange 2000/2003. In that case, defragmenting offline decreases the size of your Exchange databases by rearranging the data on the server’s Exchange databases, and discarding any unused database pages.
Note that the length of time that the defragmentation will take will depend on the amount of white space in the database, as well as the size of the transactions recorded in the database, and your hardware specifications.
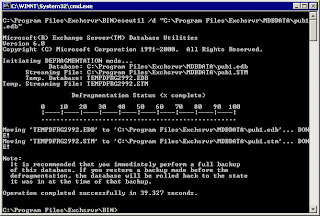
Offline defragmentation creates a new database by copying all records and tables from the old database into the new database. Because this is a copy, defragmentation requires free disk space equal to the size of the database (actually, you'll need 110% of free space).
Very important note: After defragmentation is complete, ESE considers the new database to be a different database from the original. Therefore, the original database is deleted and its member log files cannot be replayed into the successor database.
A full backup should be completed as soon as possible!
Prior incremental or differential backups are no longer useful because they reference database pages that were reordered by the defragmentation process. ESEUTIL defragments a database by creating a new database, copying the old database records to the new one, and discarding unused database pages, which results in a newly organized compact database file.
Microsoft recommends a conservative 5 - 7 GB per hour for a defrag operation, which means that your server will be offline for as long as it takes, assuming no hardware failures will occur.
When you run ESEUTIL /d against a database to defragment it, the streaming file associated with the database is automatically defragmented. This is the default behavior.
For example, if you run the following command at a command prompt:
eseutil /d "c:\program files\exchsrvr\mdbdata\priv1.edb"
The Priv1.edb and Priv1.stm files are defragmented. If you do not want the streaming file to be defragmented, include the /i option.
Run ESEUTIL with the /p switch to configure ESEUTIL to create the new defragmented database on an alternate location (for example, to a location on a different hard disk). This switch lets you preserve your original defragmented database (which lets you revert back to your original database if necessary). This switch also significantly reduces the amount of time it takes to defragment a database, because you are rebuilding to a new location, rather then rebuilding the database in place.
Note: The database you wish to defragment must be taken offline (i.e. dismounted) before attempting to perform the defragmentation operation. When you run ESEUTIL against a Microsoft Exchange computer where it's database is still mounted you will receive the following error message:
Operation terminated with error -550
If the database is still mounted, use the following steps to dismount the database, and then run ESEUTIL:
1. Start Exchange System Manager.
2. Right-click the database that you want to dismount.
3. Click All Tasks, and then click Dismount Store.

0 comments:
Post a Comment